Knowing the right medical professional to go to when you have a problem with your body is important. Just as you wouldn’t call a plumber when your oven breaks down, you need the right type of doctor or health professional when a problem with hearing loss or your ears appears. In this article we’ll focus on the differences between otologists and other related professions, and describe what each do.
When it comes to your ear problems and hearing, there are four different types of health professionals that treat patients: an ENT generalist, otologist, neurotologist or audiologist.
What is a General ENT?
An ENT (Ear, Nose and Throat) doctor is also known by the name of an otolaryngologist (ah-tow-lair-ing-ol-ah-jist). They specialize in treating diseases, tumors, and they perform surgery for trauma and deformities of the head, neck and face. The list may also include breathing difficulties, a deviated nasal septum, sinusitis, vertigo and cancer. They may perform surgical procedures and often manages situations occurring with the nerves that control facial movements, vision, the sense of smell and hearing.
An otolaryngologist’s education includes a bachelor’s degree, 4 years of medical school, and an otolaryngology 5-year residency focusing on the hearing and vestibular systems, base of the skull. They also focus on medical and surgical treatment including head and neck cancers, facial plastics and reconstruction, allergy and rhinology, and voice, and swallowing. They are certified by the American Board of Otolaryngology. Their training is more extensive in the nose and the larynx than an otologist, but an otologist has more training in the ears than a general ENT.
What is an Otologist?
The best way to describe what an otologist is and does is to compare them to a general ENT (Ear, Nose and Throat) doctor.
An otologist differs from an ear, nose and throat doctor in that they deal specifically with diseases that affect the anatomical structure of the ear, such as hearing loss from anatomical issues. They know how to treat ear inflammation, eardrums that have been perforated, dizziness, and ringing in the ears (tinnitus).
They have in-depth education on every possible detail of the ear and how it functions. An otologist is a medical doctor or surgeon that performs surgeries that affect the sensitive tissues of the ears. Every otologist may not perform surgery on ears, but most of them do.
An otologist has completed the ENT training first: a bachelor’s degree and 4 years of medical school, and then obtains further 5 years of residency training specifically on the hearing and the vestibular systems and the base of the skull. However, their training doesn’t stop there. They will take another one to three years of additional training on the evaluation and medical management of ear disorders specifically.
What is an Audiologist?
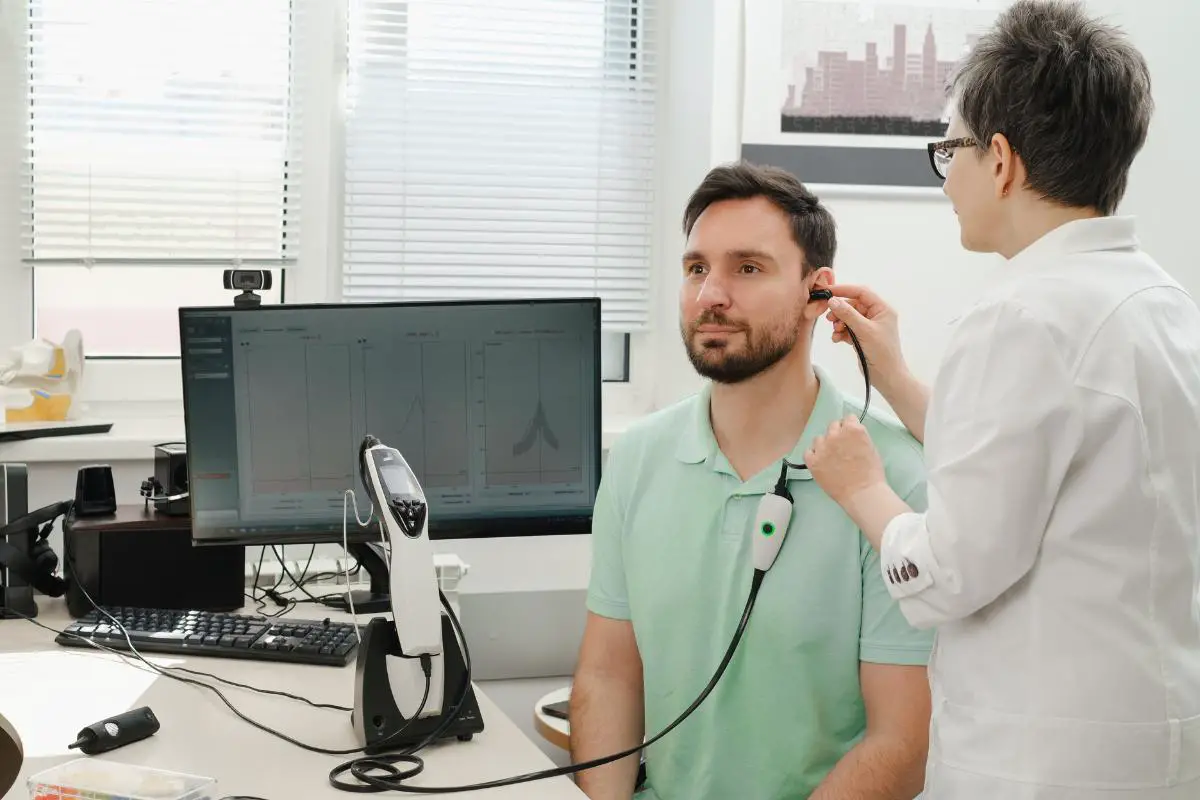
Another health professional that enters into the picture of ear and hearing disorders is an audiologist. An audiologist is a medical professional who has one of three degrees:
- a PhD in Audiology Research,
- a doctorate in Clinical Audiology, (Au.D.) or
- a Master’s degree from a university that offers training in audiology. (Note that the entry level degree for audiology is now the Au.D.)
They are trained extensively in how to use the latest technology to diagnose and measure hearing loss and other related disorders such as ringing in the ears (tinnitus) and balance disorders. In order to practice, they must become licensed in the state or commonwealth in which they intend to practice.
According to the American Academy of Audiology, audiologists are the primary healthcare professionals who evaluate, diagnose, treat, and manage hearing loss and balance disorders in individuals of all ages.
An audiologist may decide to specialize in hearing aids, cochlear implants, hearing conservation, balance disorders, evaluation and management of tinnitus and decreased sound tolerance, pediatrics, or geriatrics. You will find audiologists working at hearing aid clinics, doctors’ offices, or other medical locations, helping patients find a hearing device to meet their budget and lifestyle.
One helpful way to understand the difference between audiologists and ENT doctors or otologists is to imagine an audiologist as a hearing specialist and an ENT doctor/otologist as an ear specialist. Another way to think about it is to consider the audiologist the as the diagnostic and rehabilitative specialist and the ENT as the medical manager. Once you know that, it should be easier to figure out who to call if you have a problem with your ears.
When Do You See an Otologist?
Whether or not you need an otologist depends on what your issues are. You would make an appointment to see either an ENT or otologist for the following situations:
- You have ringing in your ears.
- Your hearing has changed recently and an audiologist or other health professional referred you.
- You have pain in your ears or a discharge. (drainage)
- Your child is suspected to have hearing problems.
- You or someone in your family has middle ear infections.
- You need surgery on your head or neck.
- You need cochlear implant surgery.
- You have something wrong with your throat, sinuses, head and/or neck.
Both an ENT and an otologist spend most of their day seeing patients, possibly performing surgery, and then taking writing medical reports or documenting information on their patients’ medical conditions. The average time spent with patients is 13-24 minutes in the office.
When Do You See an Audiologist?
You would choose an audiologist in any of the following situations:
- You feel it’s time to purchase a hearing aid.
- You (or loved ones) notice that you have difficulty communicating in noisy environments or on the phone.
- Your hearing has changed recently and needs to be checked out.
- You have ringing, buzzing, hissing, chirping, or other noises in your ears or head.
- It’s time for your hearing aids to be programmed/reprogrammed or maintained.
In today’s modern world, many seniors might first notice their need for a hearing impaired cell phone. Once the volume can’t get high enough on the phone, it might be time to check in with an audiologist. Many hearing aids can also connect directly to mobile phones via Bluetooth.
When you have booked an appointment with an audiologist, he or she will perform a series of tests to determine the cause of your hearing loss.
Anyone can pay privately for audiological services, but most insurances will pay for a patient’s assessment. This typically requires an order from their GP or ENT specialist, but any doctor’s orders for an audiogram will suffice. Normally, an audiologist in a public or private practice (such as a hospital or doctor’s office) focuses on hearing tests, hearing aids and hearing aid fittings. They will also perform adjustments and modifications as needed.
Difference Between an Otologist, Neurotologist, & Otologist Neurotologist
Both an otologist and neurotologist are accepted for a fellowship for treating ear disorders after medical school, and are both highly skilled physicians. Their jobs are closely related. The studies of otology and neurotology are often linked. In fact, many doctors are trained as both otologists and neurotologists. Their goal is to help you preserve your ability to hear, speak, and swallow, no matter what type of condition you have.
Basically, all neurotologists are otologists. But, all otologists don’t have training in neurotology. That is why some can be referred to as an otologist neurotologist. Confused yet? Think of it this way: Neurotologists have additional training in the lateral skull base area and can do lateral skull base surgery in additional to otological procedures.
What is an Otorhinolaryngologist?
Are you starting to see a pattern here? Yes, another term that is used for specialists within ENT. You may find it helpful to understand some of these words by breaking them apart into their origin. This word has greek origins, oto (ears), rhino (nose), laryn(go) (windpipe or throat), and logos (science). Meaning, the science of ears, nose, and throats.
Summary
Physicians (in this case, general ENTs, otologists, and neurotologists) diagnose and treat medical conditions and have a medical degree. Anyone experiencing pain, ear pressure, ear drainage, dizziness, sudden hearing loss, new or unilateral onsets of tinnitus, pulsatile tinnitus, or other medical concerns should pursue medical treatment from a physician. Many times, general ENT providers can diagnose and manage ear issues. If your problem requires specialized care, they will provide you with the appropriate referral.
Audiologists diagnose and manage hearing and balance concerns. If you experience a change in hearing, your first appointment should be with an audiologist. Please note that you may be required to obtain an order from a physician (this is often a primary care physician) so that your insurance will cover the testing. If medical management is needed, they will refer you to the appropriate provider. If the hearing loss does not require medical management, they will discuss your rehabilitative options.
Always follow the guidelines of your primary care physician, who will make the appropriate referrals to the health professionals you need for hearing, hearing loss, and ear issues.
FAQs
1. What body part are otologists concerned with?
They have in-depth education on every possible detail of the ear and how it functions. An otologist is a medical doctor or surgeon that performs surgeries that affect the sensitive tissues of the ears. Every otologist may not perform surgery on ears, but most of them do.
2. What is the difference between an ENT doctor and an otologist?
An otologist differs from an ear, nose and throat doctor in that they deal specifically with diseases that affect the anatomical structure of the ear, such as hearing loss from anatomical issues. They know how to treat ear inflammation, eardrums that have been perforated, dizziness, and ringing in the ears (tinnitus).
3. What is the difference between an audiologist and an otologist?
One helpful way to understand the difference between audiologists and ENT doctors or otologists is to imagine an audiologist as a hearing specialist and an ENT doctor/otologist as an ear specialist. Another way to think about it is to consider the audiologist as the diagnostic and rehabilitative specialist and the ENT as the medical manager. Once you know that, it should be easier to figure out who to call if you have a problem with your ears.
4. What is the difference between an ENT and an otolaryngologist?
Nothing! ENT (Ear, Nose, & Throat) is just a lot easier to say.
Jon Fernandez, Author
Jon is a writer, clinical author, and expert on topics related to health technology, aging, medical devices, pharmaceuticals, and skincare. He earned a Graduate Certificate in Pharmaceutical Chemistry from the University of Florida College of Pharmacy along with post graduate studies at the University of Colorado Healthcare Administration program.
Lori Zitelli, Au.D., Expert Reviewer
Dr. Lori Zitelli is an Audiology Manager at UPMC, a compensation and pension examiner at Cranberry Hearing & Balance, and an adjunct instructor at the University of Pittsburgh, where she received her clinical doctorate in Audiology. Her special interests include evaluation and treatment of tinnitus/decreased sound tolerance, amplification, clinical education, clinical research, and interventional audiology. She is a Certificate Holder in Tinnitus Management (CH-TM). Dr. Zitelli is a member/active volunteer of the American Academy of Audiology and was honored to receive the 2022 Early Career Audiologist Award.